Artificial intelligence (AI) is changing every aspect of our lives. From the ads we see, to how we unlock our devices, to how we drive our cars (or, very soon, how they drive us); nothing is off-limits. Nowhere is the impact of AI more apparent and crucial than in cybersecurity, where by the end of 2021, global cybercrime damages are predicted to cost up to $6 trillion.
The need for new technology, such as artificial intelligence, has never been more vital than it is today for cybersecurity. Here are 5 ways it is likely to help.
Topics Covered:
- Threat Detection
- Phishing Attacks
- User Authentication
- Network Security Automation
- Behavioral Analytics
Threat Detection
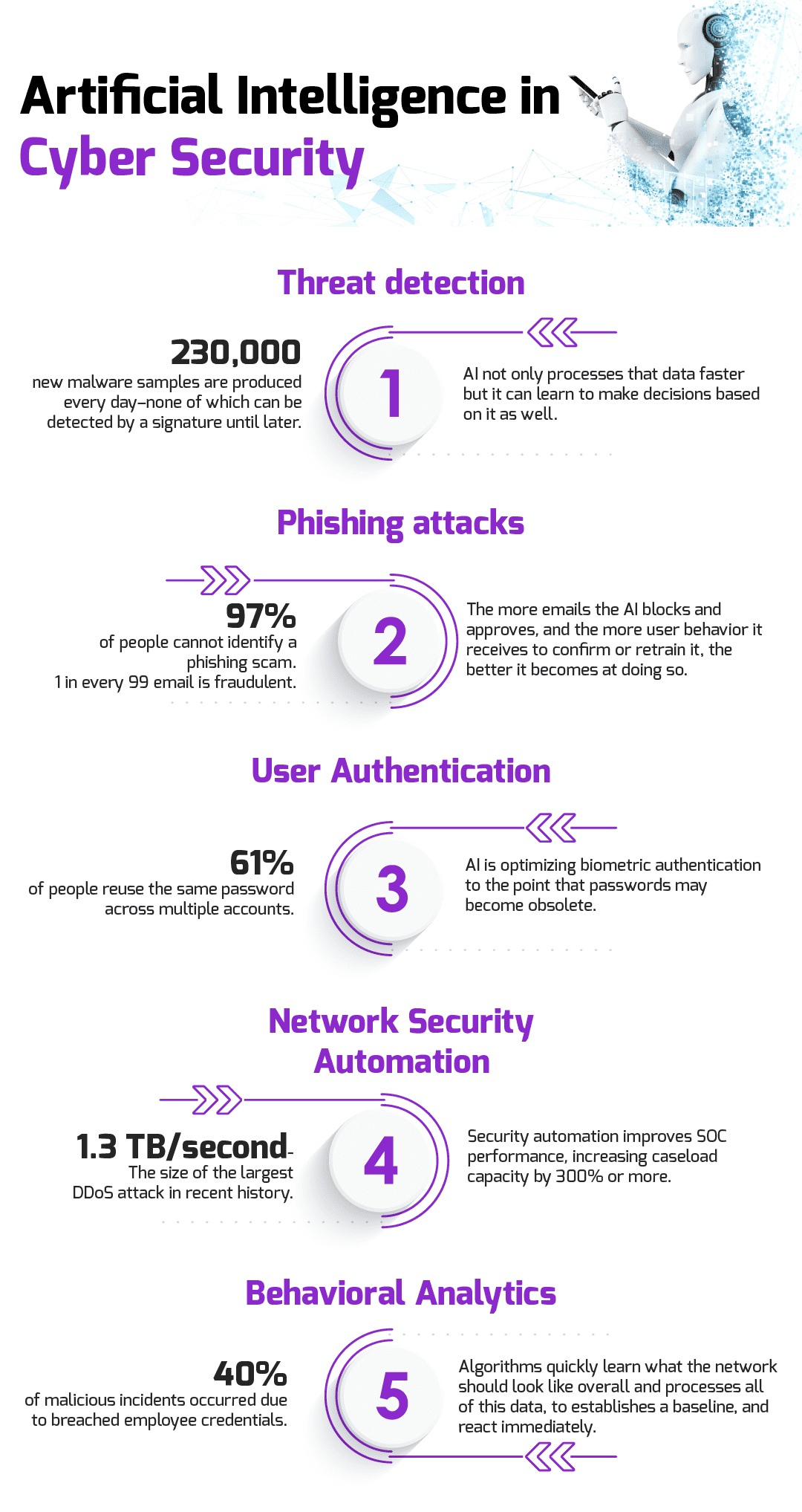
The traditional way of detecting threats is based on the past. Once the malware has been recognized and cataloged, it can be assigned a signature so that Intrusion Detection/Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS) know what to look for in the future. This works great against known threats, but what about new ones? It is estimated that 230,000 new malware samples are produced every day–none of which can be detected by a signature until later. This gap between when a new threat is detected to when it is categorized and can be prevented leaves an open window of vulnerability.
Artificial intelligence not only processes that data faster but it can learn to make decisions based on it as well. It is more accurate at detecting threats, creating less false-positives as it learns, than any human being is. Because of this, it is more adept at improvising and reacting to the endless deluge of data coming in.
Phishing Attacks
Phishing has been in existence since the early days of the internet. If it is so old, why is it still so prevalent? Because it still works. 97% of people cannot identify a phishing scam while 1 in every 99 emails are exactly that–a phishing attack. Artificial intelligence is already being used to mitigate the issue.
Artificial intelligence is able to analyze every aspect of an email, from the source to the content to the time it was sent, and react almost instantaneously to that information. It doesn’t just rely on asking, what domain did this come from? It can take into account the domain, the header, the geographic location, whether it was sent through a VPN or proxy, and compare all of that combined information against a baseline. The more emails the AI blocks and approves, and the more user behavior it receives to confirm or retrain it, the better it becomes at doing so.
Looking for career tips from Chicago’s top IT staffing team?
What is a Hiring Surge?
5 Skills Needed to be Successful in Today’s Workforce
The 4 Biggest Mistakes to Avoid When Preparing for an Interview
User Authentication
It is common knowledge that users (i.e., people) are usually the weakest link in the cybersecurity chain. Poor password habits, like reusing passwords or not changing default ones, are some of the most dangerous vulnerabilities most organizations have to face.
Artificial intelligence is optimizing biometric authentication to the point that passwords may become obsolete. Most modern mobile devices are able to use fingerprint or facial recognition to unlock a device, but today it is used mostly for convenience. Users are still hesitant to completely relinquish their login capabilities to a somewhat flawed biometric system. As these AI-power technologies get better, and new ones like voice recognition are perfect as well, passwords become less and less important.
Network Security Automation
Setting security policies and outlining network topography are two of the most time-consuming tasks of many cybersecurity engineers. That’s because most of it is done manually.
Artificial intelligence is able to automate quite a bit of this. It can monitor a network usage behavior (who accesses what, when, using how much bandwidth, etc.) and can make recommendations based on that data. A human can then review those recommendations, often much more accurate than they could have produced on their own, and make changes to policies and procedures as necessary.
Behavioral Analytics
Perhaps the most powerful way artificial intelligence can improve cybersecurity is through behavioral analytics. Seasoned cybersecurity engineers get a ‘feel’ for the networks they’re responsible for. They know them like the back of their hand—the intricacies, the nooks and crannies, the hidden compartments–no one understands these better.
Except, maybe, artificial intelligence.
Algorithms quickly learn what the network should look like overall. How much bandwidth is used on a Tuesday afternoon compared to Sunday morning? What geographic location devices are usually logging in from? What applications are accessing which ports? The algorithm processes all of this data, establishes a baseline, and can immediately react. Not only to a single event or parameter, but to a combined collection of behaviors.